基础知识
为什么需要 Hive
Hadoop 生态系统的出现,为以合理的成本处理大数据集提供了一个解决方案,它基于 HDFS(分布式文件系统)实现了一个 MapReduce 编程模型,将计算任务分散到多个硬件机器上,从而降低成本并提供水平伸缩性。
但是从现有的数据基础架构转移到 Hadoop 以及从 Hadoop 中获取数据是一个比较麻烦的事情(MapReduce Java API),Hive 的出现就是为了解决这个问题,基于 Hive 可以方便的实现结构化数据到 Hadoop 数据仓库的数据转移。
Hive 将大多数的查询转化成 MR 任务,HiveQL 既降低了使用难度,也提高了 Hadoop 的扩展性。
Hive 的局限
- Hive 适用于数据不经常变动,而且不需要立即得到查询结果的情况。
- 由于 Hadoop 和 HDFS 的设计,Hive 不支持行级别的插入、删除及更新,不支持事务。
- HiveQL 不符合 ANSI SQL 标准,很多 SQL 和 Oracle、MySQL 存在差异。
Java 和 Hive :词频统计算法
这是《Hadoop权威指南》中的第一章的例子程序,使用 Hadoop Java API 实现一个统计文本文件中每个单词出现次数的程序,可以帮助理解 MR 原理以及使用 Hive 的好处。
关键代码如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-hdfs</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-mapreduce-client-core</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
package im.yuki.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author longkun
* @version V1.0
* @date 2022/3/17 11:36 PM
* @description hadoop 词频统计
*/
public class WordCount {
private static final String OUTPUT_PATH = "hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/hdp/0317/wordcountoutput/";
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable> {
private static final LongWritable one = new LongWritable(1);
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
Text word;
for (String w : words) {
word = new Text(w);
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
int count = 0;
for (LongWritable value : values) {
count += value.get();
}
context.write(key, new LongWritable(count));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
// 设置环境变量 HADOOP_USER_NAME
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "longkun");
// 读取配置文件
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.set("fs.defaultFS", "hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000");
configuration.set("yarn.resourcemanager.hostname", "hdp01");
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(configuration);
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration, "WordCount");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
Path outputPath = new Path(OUTPUT_PATH);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/hdp/0317/wordcountinput/"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
if (fileSystem.exists(outputPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outputPath, true);
}
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
⚠️ 运行时会提示 log4j 的配置有误,运行程序前需要将 $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/log4j.properties 文件复制到 src/main/resouces 目录下。
将需要统计的文本文件上传到 hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/hdp/0317/wordcountinput 目录下。
在 Hive 中统计词频:
1、将文本文件上传到 hdfs 中
hdfs dfs -put ~/Desktop/wordcount.txt /hdp/0317/wordcountinput
2、将 hdfs 中的数据插入到 Hive 表中
> load data inpath '/hdp/0317/wordcountinput/wordcount.txt' docs
3、HiveQL 查询结果
select tmp.word, count(*) as cnt
from (
select explode(split(line, ' ')) as word
from docs
) tmp
group by tmp.word
order by cnt;
Hive 命令
执行 hive --help 查看 Hive 命令列表:
| 选项 | 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| cli | 命令行界面 | 进入命令行。 |
| hwi | Hive Web 界面 | 可以执行查询语句和其他命令的简单 Web 界面。 |
| metastore | 启动一个扩展的元数据服务,可以供多客户端使用。 | |
| rcfilecat | 一个可以打印出 RCFile 格式文件内容的工具 |
CLI 选项
使用命令 hive --help --service cli 查看 cli 选项。
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| -d | –define | 变量替换 |
| -e | 执行命令行中的 SQL |
| -f | 从文件中执行 SQL |
| -H | 打印帮助信息 |
| -h | 连接主机名 |
| -i | 初始化 SQL 文件 |
| -p | 连接端口 |
| -S | -silent | 交互式命令行下安静模式 |
| -v | –verbose | 输出调试信息 |
Hive 的属性命名空间
| 命名空间 | 权限 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| hivevar | 可读可写 | 用户自定义变量 |
| hiveconf | 可读可写 | Hive 相关的配置 |
| system | 可读可写 | Java 定义的配置属性 |
| env | 只可读 | Shell 环境定义的环境变量 |
几个例子🌰:
# hivevar --define & set
$ hive --define foo=bar;
> set foo;
> foo=bar;
> set hivevar:foo=bar2;
> create table tbl_0318(int i, ${foo} string);
> desc tbl_0318;
OK
i int
bar2 string
# hiveconf
# 显示当前所在库名
> set hiveconf hive.cli.print.current.db=true;
# system
> set system:user.name
system:user.name=longkun
# env
> set env:HOME
env:HOME=/Users/longkun
Hive 中使用一次命令
✅ 如果希望一次执行多个查询,查询结束后立即退出 cli,可以使用 -e 选项:
$ hive --service cli -e "select * from db_0316.docs where 1 = 1";
✅ 还可以将输出重定向到一个文件中:
$ hive --service cli -e "select * from db_0316.docs where 1 = 1" > ~/Desktop/hive_tmp_result.txt
✅ 当记不清楚某个属性名时,可以使用 grep :
$ hive -S -e "set" | grep current.db
hive.cli.print.current.db=false
$ hive -S -e "set" | grep warehouse
hive.metastore.warehouse.dir=/user/hive/warehouse
从文件中执行查询
可以使用 -f 选项从文件中执行一个或多个查询语句,文件尽量使用 .q 或者 .hql 后缀。
新建一个文本文件 query.hql:
select *
from db_0316.docs
where 1 = 1;
# 执行查询
$ hive -S -f query.hql
# 在 cli 中可以使用 source 命令来执行文件中的查询语句
> source ~/Documents/Hive/query.hql
hiverc文件
-i 选项执行一个文件,每次 CLI 启动时会先执行这个文件。Hive 会在当前目录下寻找 .hiverc 文件并执行。编辑 $HIVE_HOME/.hiverc 文件,添加几个比较实用的变量(⚠️ 分号是必须的):
set hive.cli.print.current.db=true;
set hive.cli.print.header=true;
set hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true;
✅ 使用 tab 键可以补全关键字或者函数名。
执行 shell 命令
无需退出 cli 即可执行简单的 shell 命令,只需要在 shell 命令前加上 ! ,并且以 ; 结尾。
hive (default)> !pwd;
/Users/longkun
在 Hive 内使用 dfs 命令
用户可以在 cli 中执行 Hadoop 的 dfs 命令,只需要将 hdfs 去掉。
hive (default)> dfs -ls /;
Found 3 items
drwxr-xr-x - longkun supergroup 0 2022-03-17 23:54 /hdp
drwx-wx-wx - longkun supergroup 0 2022-03-18 00:52 /tmp
drwxr-xr-x - longkun supergroup 0 2022-03-16 21:50 /user
据说这种方式比在 bash shell 中执行 hdfs dfs … 更高效,因为后者会每次启动一个 JVM 实例,而 Hive 会在同一个进程执行。
数据类型和文件格式
byte、Byte、bit、字节
bit
bit 即是位,表示一个二进制位,0 或 1。byte
Java 的基本数据类型之一,存储整形,Byte 是其包装类。Byte
Byte 表示字节,1 Byte = 8 bitHive 中的数据类型都来源于 Java 中的数据类型。
Hive 中的数据类型
| 数据类型 | 长度 | 例子🌰 |
|---|---|---|
| TINYINT | 1byte 有符号整数 | 20 |
| SMALLINT | 2byte 有符号整数 | 20 |
| INT | 4byte 有符号整数 | 20 |
| BIGINT | 8byte 有符号整数 | 20 |
| BOOLEAN | bool类型,true 或者 false | TRUE |
| FLOAT | 单精度浮点型 | 3.1315 |
| DOUBLE | 双精度浮点型 | 3.1415 |
| STRING | 字符序列,可以使用单引号或者双引号 | ‘zhang san’ “wang er” |
| TIMESTAMP | 整数、浮点或者字符串 | Unix新纪元秒,Unix新纪元秒及纳秒,JDBC时间格式 |
| BINARY | 字节数组 | 和关系型数据库中 VARNIBARY类似?没看懂 |
单精度和双精度是什么意思?单和双是什么意思?
单精度:1位符号,8位指数,23位小数。

双精度:1位符号,11位指数,52位小数。
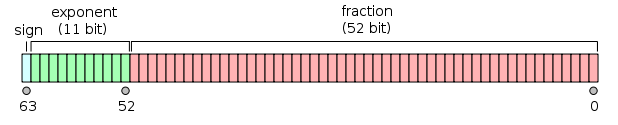
还是没解释 单 和 双 的意思。。
集合类型
Hive 中支持 struct、map 和 array 集合数据类型。
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| STRUCT | 与对象类似,可以通过 . 访问元素内容 | struct{first string, last string} |
| MAP | 键值对 | map(‘first’, ‘john’, ‘last’, ‘doe’) |
| ARRAY | 具有相同类型的变量集合 | array(‘first’, ‘last’) |
建表语句:
drop table if exists db_0320.tbl_person;
drop table if exists db_0320.person;
create table db_0320.tbl_person (
name string comment 'name',
age float comment 'age',
location string comment 'location',
friends array<string> comment 'friends',
score map<string, double> comment 'score',
address struct<number: tinyint, street: string, city: string>
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by '\001'
collection terminated by '\002'
map keys terminated by '\003'
lines terminated by '\n'
stored as textfile;
HiveQL 数据定义
概览
- HiveQL 和 MySQL 比较接近,但也有较大差异
- Hive 不支持行级插入、更新及删除操作
- Hive 不支持事务
- 大多数情况下 HiveQL 和其他 SQL 很像
- 查询、分组、过滤及连接
常见查询
-- 新建数据库
> create database db_test;
> create database if not exists db_test;
-- 查看所有的库
> show databases;
-- 使用正则表达式
-- 查询以 db_ 开头 的所有数据库
> show databases like 'db_*'
-- 查看库里的表
> show tables from db_test;
-- 删库(删库之前必须先删除库中的表,或者使用关键字 CASCADE)
> drop database if exists db_test cascade;
-- 查看表属性
> desc formatted tbl_test;
-- 如果只想查看某一列的信息,只需在表名后增加这一列的名称即可(亲测报错:missing EOF at '.' near 'tbl_person')
> describe db_0320.tbl_person.score;
-- 拷贝一张已存在的表
> create table if not exists tbl_test1 like tbl_test;
内部表与外部表(MANAGED_TABLE & EXTERNAL_TABLE)
使用 EXTERNAL 创建的表是外部表,否则就是内部表。内部表默认存储在 user/hive/warehouse/下, 当删除一个表时,Hive 会删除该目录下存储的数据;而删除外部表时,只会删除表的元数据,不会删除表数据。严格说,Hive 管理着这么目录和文件,但是不对其拥有完全控制权。
外部表示例:
1、先建立一个目录,存放外部表要操作的数据
> dfs -mkdir /hdp/0322
2、建表并指向外部表空间
drop table if exists db_0320.ex_tbl_student;
create external table if not exists db_0320.ex_tbl_student (
name string comment 'name',
age float comment 'age',
class string comment 'class'
)
row format
delimited fields terminated by ','
location '/hdp/0322/';
3、准备数据并上传至 HDFS
> dfs -put ~/Documents/ex_tbl_student.txt /hdp/0323/
文件内容:
zhangsan,12,一班
lisi,14,二班
wangwu,16,三班
4、将数据导入外部表中
> load data inpath '/hdp/0323/ex_tbl_student.txt' overwrite into table db_0320.ex_tbl_student;
5、确认数据及操作
分区表和管理表
分区将数据分散在多个目录下,可以提高查询性能。
如果表中数据或者分区中的数据量巨大,执行一个包含所有分区的查询会出发巨大的 MR 任务,可以将 hive.mapred.mode=strict 设置成严格模式禁止提交任务。
创建分区表:
drop table if exists db_0322.tbl_student;
create table if not exists db_0322.tbl_student (
name string comment 'name',
age float comment 'age',
class string comment 'class'
)
partitioned by (grade string comment 'grade');
查看分区:
> desc partitions db_0322.tbl_student;
导入数据至分区表:
> load data inpath 'tbl_student.txt' overwrite into table tbl_student partition (grade='grade2');
为外部分区表增加一个分区:
> alter table log add partition(year=2012, month=1, day=1);
对表的操作
删除表:
> drop table if exists db_0323.tbl_test;
可以了解下 Hive 的回收站功能。
修改表:可以使用 alter table 语句修改表,这种方式会修改表的元数据,不会修改数据本身。
-- 重命名表
> alter table tbl_test rename to tbl_test1;
-- 增加分区,给没有分区的表添加分区会报错
> alter table tbl_test add if not exists partition (city='Beijing');
-- 删除分区
> alter table tbl_test2 drop if exists partition (city = 'Beijing');
-- 修改字段
> alter table tbl_test2 change column name username string comment 'username' after column1;
-- 新增一个字段
> alter table tbl_test1 add columns (age float comment 'age');
-- 修改表属性
> alter table tbl_test1 set tblproperties ('note'='test note....')
-- 执行钩子,当往表中写入数据时触发执行
> alter table tbl_test touch partition(year=2021, month=12, day=1);
-- 将分区内的文件打包成 Hadoop 压缩包(HAR),使用 unarchive 反向操作
> alter table ... archive partition (year, month, day);
-- 防止分区被修改或删除(报错)
> alter table tbl_test partition (year=2021, month=10, day=1) enable no_drop;
HiveQL 数据操作
Hive 不支持行级数据插入、更新及删除,只能通过大批量的方式将数据导入表中。
> load data local inpath '${env:HOME}/data' overwrite into table tbl_test partition (year = 2022, month = 3, day = 22);
local 表示本地目录,如果不加 local 则表示 hdfs 上的文件。
Hive 不会校验导入的数据和表的模式是否匹配,但是会校验文件格式是否和表的定义一致。
通过查询向表中导入数据:
use db_0323;
from tbl_test3_tmp tmp
insert overwrite table tbl_test3
partition (city = 'Beijing')
select name where tmp.city = 'Beijing'
insert overwrite table tbl_test3
partition (city = 'Tianjin')
select name where tmp.city = 'Tianjin'
insert overwrite table tbl_test3
partition (city = 'Tianjing')
select name where tmp.city = 'Tianjing';
如果一个分区一个分区的查出来再导入的话,会非常繁琐,可以使用动态分区插入来避免这个问题。
use db_0323;
insert overwrite table tbl_test3
select name, city
from tbl_test3_tmp;
最后的几列顺序要和分区字段一致,Hive 根据列位置来确定分区字段,而不是名称。并且静态分区字段必须位于动态分区字段之前。
dfs -ls /user/hive/warehouse/db_0323.db/tbl_test3 查看分区:
Found 3 items
drwxr-xr-x - longkun supergroup 0 2022-03-24 23:56 /user/hive/warehouse/db_0323.db/tbl_test3/city=Beijing
drwxr-xr-x - longkun supergroup 0 2022-03-24 23:56 /user/hive/warehouse/db_0323.db/tbl_test3/city=Tianjin
drwxr-xr-x - longkun supergroup 0 2022-03-24 23:56 /user/hive/warehouse/db_0323.db/tbl_test3/city=Tianjing
动态分区功能默认是关闭的。开启后,默认以“严格”模式执行,这种模式下,要求至少有一列字段是静态分区,有助于防止因设计错误导致产生大量的分区。
动态分区相关属性:
| 属性名称 | 缺省值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| hive.exec.dynamic.partition | false | 设置成 true,开启动态分区功能 |
| hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode | strict | 设置成 no strict,允许所有列都是动态分区 |
| hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode | 100 | 每个 mapper 和 reducer 可以创建的最大分数,超过会报错 |
| hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions | 1000 | 一个动态分区语句可以创建的最大动态分区个数,超过会报错 |
| hive.exec.max.created.files | 100000 | 全局可以创建的最大文件个数,超过会报错 |
单个查询语句创建表并加载数据:
create table tbl_test4 as
select name
from tbl_test3
where city = 'Beijing';
导出数据 insert directory:
use db_0323;
-- 第一种方式
insert overwrite local directory '${env:HOME}/Documents/Hive/export'
select name, city
from tbl_test3
where city = 'Beijing';
-- 第二种方式
from tbl_test3 tmp
insert overwrite local directory '${env:HOME}/Documents/Hive/export-beijing'
select name where tmp.city = 'Beijing'
insert overwrite local directory '${env:HOME}/Documents/Hive/export-tianjin'
select name where tmp.city = 'Tianjin'
insert overwrite local directory '${env:HOME}/Documents/Hive/export-tianjing'
select name where tmp.city = 'Tianjing';
Hive 中没有临时表的概念。
HiveQL 查询
常用函数:
| 返回值类型 | 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| BIGINT | round(double d) | 取近似值 |
| DOUBLE | round(double d, int n) | 取近似值,保留 n 位小数 |
| BIGINT | floot(double d) | 向下取整 |
| BIGINT | ceil(double d) | 向上取整 |
| DOUBLE | rand() | 生成一个 DOUBLE 类型的随机数 |
| STRING | concat_ws(string separator, string s1, string s2…) | 使用指定的分隔符连接字符串 |
| STRING | substr(string s, int start, int length) | 截取子字符串 |
| STRING | to_date(string date) | ‘2022-01-01 10:20:12’ -> ‘2022-01-01’ |
| INT | year(string date) | 返回年 |
| INT | month | 获取月份 |
| INT | date_diff(string date1, string date2) | 获取两个日期相差天数 |
| INT | date_add(string date, int days) | 日期相加 |
| INT | date_sub(string date, int days) | 日期相减 |
嵌套 SELECT
from (
select name, age
from tbl_test3
where age > 10
) tmp
select tmp.*
where tmp.name like 'zhang%';
CASE WHEN
select name,
case
when age < 18 then '未成年'
when age >= 18 and age < 60 then '成年'
else '老年'
end as age,
sex
from tbl_test;
避免进行 MapReduce
- where 条件中过滤字段是分区字段
- 没有 where 条件的 select 语句
- hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true 会尝试本地模式执行其他 SQL
类型转换 cast
最好使用 ceil / floor / round 等函数来将字符串转为整数。
抽样查询
按照(基于行数的)百分比进行抽样。
select * from tbl_student_info_tmp tablesample(50 percent);
UNION ALL
将多个子表进行合并,这几个子表的列及顺序及类型必须完全一致,理论上可以改为多个 where 语句。
HiveQL 视图
可以使用视图简化查询:
-- 所有来自北京的学生
create view view_student_beijing as
select uid, name, age, grade, class
from tbl_student_info
where home_address.province = '北京';
-- 来自北京年龄小于 20 的学生
select *
from view_student_beijing
where ceil(age) <= 20;
删除视图:
drop view if exists view_student_beijing;
视图不能做为 load 和 insert 的目标表。视图是只读的,只允许改变与数据信息 tblpropreties。
alter view set tblproperties('created_by'='system');
HiveQL 索引
模式设计
分区表
随着系统运行时间的增加,表数据量会越来越大,Hive 查询通常是全表扫描,性能会越来越低。可以使用分区表提高性能。
create table tbl_test(name string)
partitioned by (kind string);
分区列只是一个目录名称,实际不存储这一列数据。
应该选择合适的分区字段,如果分区数太大,会创建大量的 Hadoop 文件及文件夹,反而会降低查询效率。
可以选择多个分区字段来进行分区。
create table student (
name string,
sex string
) partitioned by (grade string, class string);
查看分区:
show partitions table_name;
唯一键和标准化
Hive 没有关系型数据库中的唯一键和序列自增,应避免对非标准化(?)数据进行 JOIN 操作,复杂的数据类型,可以通过 Array、Map、STRUCT 实现。
同一份数据处理多次
Hive 可以从一个数据源产生多个数据聚合,而无需每次聚合都重新扫描一次,可以节省很多时间。
from tbl_student_info_tmp
insert overwrite tbl_student_info1 where age > 10;
insert overwrite tbl_student_info2 where age > 20;
对于每个表的分区
对于一些中间数据可以使用分区,可以保证任务重跑的时候不会覆盖所有的数据,只对目标数据进行处理。
这几个月负责公司一些数据的处理,基本都是按月拉结果,使用月末的时间做为分区,这样每一个月的数据都可以留存下来成为历史数据,不受下个月数据的影响。
分桶 🪣
Hive表分区的实质是分目录(将超大表的数据按指定标准细分到指定目录),且分区的字段不属于Hive表中存在的字段;分桶的实质是分文件(将超大文件的数据按指定标准细分到分桶文件),且分桶的字段必须在Hive表中存在。
分桶的好处在于表中的数据已经按条件分到了多个文件中,join 或者其他计算时只需取符合条件的数据进行处理,从而提高性能。
-- 创建分桶表
use db_0327;
drop table if exists bucket_tbl_student_info;
create table if not exists bucket_tbl_student_info (
uid string comment 'uid',
name string comment 'name',
age int comment 'age'
) clustered by (age) into 2 buckets
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
lines terminated by '\n';
-- 将数据写入分桶表
set hiveconf:hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
use db_0327;
from tbl_student_info_tmp
insert overwrite table bucket_tbl_student_info
select uid, name, floor(age) as age where 1 = 1;
-- 如果不设置 hiveconf:mapred.reduce.tasks,则需要手动设置与分桶个数相等的 reducer 数
set hiveconf:mapred.reduce.tasks=2;
use db_0327;
from tbl_student_info_tmp
insert into table bucket_tbl_student_info
select uid, name, floor(age)
where 1 = 1
cluster by age;
-- 从分桶表中获取抽样数据
select uid, name, age from bucket_tbl_student_info tablesample(bucket 1 out of 2 on age);
将 hive.enforce.bucketing 设置成 true 之后,Hive 会在目标表初始化过程中设置一个正确的 reducer 数。
为表新增列
Hive 表对数据格式的要求比较宽松,列的信息在元数据中,新增列或者删除列只是改变元数据。如果列的个数比实际数据的列要多,则多余的列会被省略,相反,则会以 NULL 填充。
Hive 表新增列:
alter table tbl_access_log add columns (rank1 int, rank2 int);
在新增列之前入库的数据,查询的时候新加的字段会用 NULL 填充。
使用列存储表 📦
Hive 默认使用行式存储。假设有足够多的列,列中有很多的重复数据,这种类型的数据使用列式存储性能会更好,查询的时候不要加载所有列的数据。
参见 15.3.2 RCfile 使用这种格式?
使用压缩 🗜️
几乎所有的情况下,使用压缩都能降低磁盘占用量,降低 I/O 以提高查询速度。
使用外部数据或者非压缩格式时无法使用压缩。
压缩和解压缩都会消耗 CPU 资源,但是大多数 MR 任务都是 I/O 密集型任务,所以 CPU 开销通常不是问题。
Hive 常见问题及解决方案记录 📝
1、启动 Hive 报错:Cannot create directory /tmp/hive/longkun/50be98c2-62e0-4b37-9002-c2270fed6a20. Name node is in safe mode.
控制台日志提示无法创建临时目录,Hive 处于安全模式中。
安全模式主要是 HDFS 系统的时候检查 DataNode 上数据块的有效性,同时根据策略复制和删除部分数据块,运行的时候也可以通过命令进入安全模式。安全模式中不允许修改和删除数据。
可以通过命令来离开安全🔐模式:
hadoop dfsadmin -safemode leave离开安全模式之后,Hive 正常启动。